There are many types of chemicals used in the home such as bath soaps, shampoos, detergents, ... all of which are at risk of harm to children. Drinking the wrong household chemicals is a common accident in young children
Signs of a child with chemical poisoning Gastrointestinal
signs: Child has a sore throat, nausea and vomiting, red lips and tongue, blistering, bleeding, localized pain in the epigastric region, nose sternum or spreading pain throughout the abdomen.
Respiratory signs: Children with shortness of breath, rapid breathing, pale face, bulging nose wings, and spasm of the respiratory muscles in the neck, the snout are all manifestations of respiratory failure. In addition, a hissing sound can be heard due to laryngospasm.
Other signs: pale skin, pale, sometimes purple blotches; Children with chemical poisoning can have a disorder of consciousness, panic and cry, but may also be comatose.
First aid First, give the child water or milk to dilute the toxin. Most of the cases of mistakenly drinking are household chemicals such as bath soap, shampoo, dish soap, just give the child plenty of water or milk to dilute chemicals, reduce irritation to the mucosa. Give your child plenty of drinks but take it slowly to avoid choking.
Next, if the child is awake, does not fall into a coma, it is necessary to induce vomiting. Take about 200-300ml of 0.9% salt water for children to drink, and then swab your throat with your hands to let them vomit chemicals. Do not induce vomiting when ingested with corrosive chemicals (acids, bases or gasoline)
In addition, it is possible to use protective substances for the gastric mucosa such as flour, rice flour, milk, egg whites, porridge ... to prevent the absorption of toxins from the stomach and intestines. If metal poisoning (lead, mercury ...) can use egg whites, milk or 4 - 10g sodium sulfate to create precipitation reactions, limiting the effects of the poison.
After giving first aid to a child, parents need reassurance so that the child is not afraid and cooperate to help learn and handle correctly. Check the chemicals in the house to determine the names of chemicals that the child has taken, ask them many times to identify and check the information about chemicals, quantity, time to drink and other related information. .
When the child was given first aid, but the child was still in a state of respiratory failure, abnormal pulse, hypotension, sweating, it should be quickly referred to the hospital for prompt treatment.
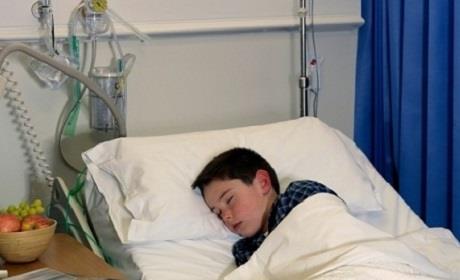
Quickly take your baby to the hospital if he has signs of poisoning with harmful chemicals.
Preventing chemical poisoning for babies
Household chemicals must be kept in private places, out of reach of children. Highly toxic substances (paint solvents, insecticides such as mosquito sprays ...) need to be stored in separate, locked places that cannot be accessed by children.
Do not store drinks in bottles that previously contained chemicals. In contrast, do not put chemicals in the bottles that contain drinking water that can easily cause confusion.
Do not leave any chemicals in the area where babies often play around. In particular, do not let children play by themselves.