The effects of uterine fibroids may make it harder to conceive than normal and have problems during pregnancy.
Fibroids are the abnormal growth of muscle cells and fibrous tissue, thereby forming a tumor in the uterus. According to the National Institutes of Health , 70-80% of women will have fibroids at the age of 50 and 20-50% of women of childbearing age have the condition. However, the good news is that most cases of uterine fibroids are not malignant and do not require any medical intervention.
1. Cause
The cause of uterine fibroids is not known, but it is believed to be related to estrogen and progesterone levels because these hormones are made in a woman's ovaries. That explains why uterine fibroids sometimes grow in larger sizes during pregnancy, in part because the production of these two hormones peaks and then the fibroids shrink again once the woman is already pregnant. birth. There are three types of fibroids:
Intramural: This is the most common form of fibroids and usually located in the wall of the uterus
Submucosal: This is a fibroid that forms and develops in the lining of the uterus
Subserosal: This is a fibroid that forms and develops outside the uterus.
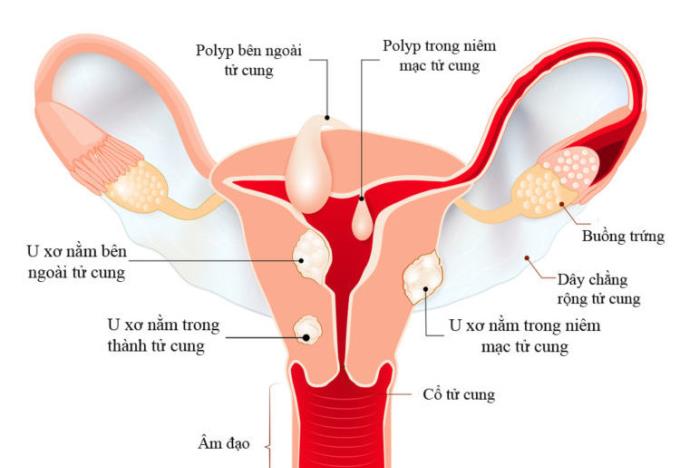
2. Identification mark
Many women do not even know they have a fibroid because it is asymptomatic. In addition, severe fibroid cases will appear some of the following signs:
Menstruation is long, thick, and painful when it comes to periods
Painful feelings every time sex
A feeling of pressure in your back, bladder, or intestines
Occurrence of blood spots even though the period has not yet arrived
Have fertility problems, including infertility , miscarriage, and preterm birth
Urinate often
Having trouble going to the toilet.
You can be diagnosed with fibroids through an examination of the pelvic area. If your doctor suspects an abnormal tumor is not necessarily cancerous, you will need to use an ultrasound to confirm that this is a fibroid and not any other risk.
3. The effect of uterine fibroids on pregnancy

Most women will experience the effects of uterine fibroids during pregnancy. However, a 2010 review found that 10-30% of women with uterine fibroids develop complications during pregnancy. The researchers also noted that the most common complication of fibroids is pain. In addition, fibroids larger than 5cm in size are also easily seen in the last 2 trimesters of pregnancy.
The effects of uterine fibroids also increase your risk of other complications during pregnancy and childbirth, such as:
Limiting fetal growth: Large fibroids can prevent the fetus from developing completely due to the gradually narrowed uterine area.
Premature placenta: This occurs when the placenta separates from the uterine wall because it is blocked by fibroids, reducing the amount of oxygen and vital nutrients that are transferred to the uterus.
Premature: Pain caused by fibroids can lead to uterine contractions leading to preterm delivery.
Caesarean section: It is estimated that women with fibroids are 6 times more likely to have a cesarean section than women without developing fibroids.
An inverted fetus: The abnormal shape of the womb can prevent the baby from being delivered through the vagina
Miscarriage: Doctors also note that due to the effects of fibroids, pregnant mothers are 6 times more likely to have miscarriage than normal people.
4. Effects of pregnancy on uterine fibroids
Most tumors have no change in size during pregnancy, but exceptions are still present. In fact, one-third of uterine fibroids can develop in the first trimester due to the effects of estrogen and increased estrogen levels during pregnancy.
However, for other women, fibroids can actually shrink during pregnancy. In a study done in 2010, doctors found that 79% of uterine fibroids that appeared before pregnancy decreased in size after birth.
5. The effect of uterine fibroids on fertility
Many women with uterine fibroids can get pregnant spontaneously, even though interventions are considered unnecessary. However, in some cases, uterine fibroids can affect your fertility. For example, submucosal fibroids are fibroids that grow and bulge large into the uterine cavity, increasing the risk of infertility or miscarriage.
If you have trouble conceiving or maintaining a pregnancy, your doctor will consider any possible cases before suggesting a fibroid problem.
6. How to overcome the effects of uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids are usually not treated during pregnancy unless severe symptoms, such as excessive bleeding or chronic pain, are present. If the fibroids are not causing unpleasant symptoms, your doctor will leave them alone and monitor them periodically. In addition, uterine fibroids are also treated with:
Medications: Fibroids may also decrease in size after a cycle of hormone changes or drug effects.
Arterectomy: A small tube will be inserted into the artery supplying the fibroids with blood and small particles are injected to stop the blood flow, thereby causing the tumor to die and completely disappear.
Laparoscopy: A small catheter that penetrates the body through the stomach to remove a fibroid.
Surgery: This is for large tumors only.













