If you are looking for safe and effective methods of contraception while breastfeeding, please refer to the article of aFamilyToday Health!
If you are looking for methods of contraception that are both effective and safe while breastfeeding , please refer to the article below.
How to prevent pregnancy while breastfeeding?
You may have heard that while breastfeeding is the best contraceptive period, this is only partially true.
Breastfeeding reduces the chances of getting pregnant only if you are exclusively breastfed and the method is only reliable for 6 months after the baby is born. To do this method, you must feed your baby at least once every 4 hours during the day and every 6 hours at night, and do not give your baby anything else. This means that the baby gets nothing but breast milk.
After the baby is born, you will ovulate and then if you are not pregnant you will have your first menstrual period about 2 weeks later. You may not even know you are ovulating. Therefore, you are still at risk of becoming pregnant while breastfeeding. This method will not work if your period has returned.
If you are concerned about contraception while breastfeeding, you should talk to your doctor about your options because you will most likely want to avoid using birth control methods that contain the hormone estrogen (which reduces milk provided for lactation).
Contraceptive methods when breastfeeding
1. Natural contraception
There are many ways to practice family planning. Pay close attention to your body's circadian rhythm and don't forget to calculate your menstrual cycle. A typical menstrual cycle lasts between 26 and 32 days. In addition, you will need to watch for cervical mucus secreting from the vagina.
You can also take your temperature every morning with a special thermometer. This will help you see the increase or decrease in your body temperature and know your ovulation period, because when you ovulate your body temperature tends to increase.
However, it is difficult to predict when you will have a baby again after giving birth. Most women after ovulation begin to experience no menstruation . In addition, your first menstrual cycle may be irregular and different from previous periods.
If you choose this method, please find out the information carefully. In addition, you need to be diligent in monitoring your mucus, monitoring your calendar, symptoms, and temperature. The effectiveness of the natural plan method is about 76% or less if you don't practice this method consistently.
This is not a good choice for women with irregular periods. Also, your cycle can be very unpredictable while breastfeeding. Consider using a backup method such as a condom, cervical cap, or diaphragm.
2. Use birth control pills while breastfeeding

Traditional birth control pills contain a mixture of the hormones estrogen and progestin. Because of this mixture, some women may experience a decrease in the amount of milk and therefore a shorter time to breastfeed when using combined oral contraceptives. Experts believe that estrogen is the root cause of this.
If you want to take oral contraceptive pills, minipills must be a great choice. This pill contains only progestin. Therefore, this drug is believed to be safer for mothers who breastfeed their babies. This pill is usually only prescribed by prescription, but can still be bought over a number of drugstores.
Each pill in a pack of 28 contains a progestin that will keep you from having periods for 1 month. You may experience unusual bleeding or bleeding as your body tries to adjust to the birth control pill.
Like many other progestin-containing birth control pills, you can start minipills between 6 and 8 weeks after your baby is born. It has a contraceptive efficacy of 87 - 99.7%.
This method helps you to be successful at birth control if you remember to take your pill at the same time every day to keep hormone levels steady.
Side effects
When taking minipills, you may experience side effects such as headaches, unusual bleeding to decreased libido or ovarian cysts . If you decide you want to get pregnant again after taking this medication, consult your doctor. Some women are still able to conceive again soon after stopping the drug or it can take several months for their body to return to the same body.
Many people find that even using any hormonal method of birth control their milk supply will decrease. To overcome that, you should breastfeed more and express regularly during the first few weeks of taking the medicine. If your breast milk supply continues to decline, talk to your doctor for instructions on how to increase your milk supply.
3. The contraceptive injection Depo-Provera
Depo-Provera injection is a long-term prescription for birth control. It uses the hormone progestin to prevent pregnancy. This injection is effective to prevent pregnancy for up to 3 months. So, if you do not continue the injection after 3 months, the contraceptive effect will be lost. This method is about 97% effective. If every 12 weeks you inject drugs on time, the drug will be more effective than those who quit or do not follow the correct schedule.
Side effects of the Depo-Provera contraceptive injection include abdominal pain to headache or weight gain. Some people may also develop osteoporosis while using this birth control method. If you want to have a baby, it's important to note that it may take 10 months or longer for your fertility to return to normal after you stop using this method.
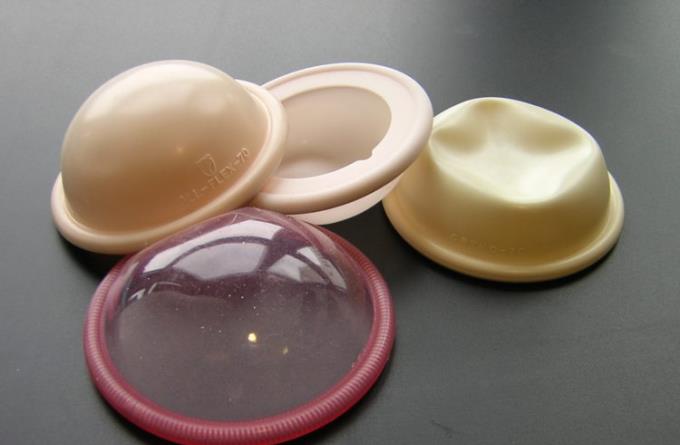
4. Contraceptive sponge
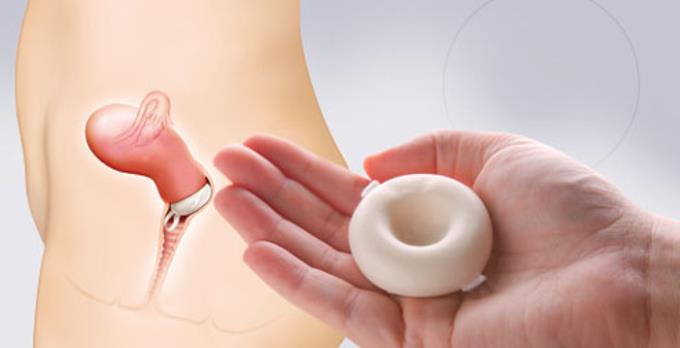
This is a polyurethane sponge used to insert into the vagina to help prevent pregnancy. The sponges will keep sperm from entering your uterus. When used normally, this method of contraception is about 88% effective, but may be less effective for mothers who have already had a baby.
The contraceptive sponge contains spermicides, so it not only prevents sperm from reaching the uterus, but also contains chemicals that help inactivate and kill sperm. You should keep the contraceptive sponge in your vagina for at least 6 hours after sex, but don't leave it in there for more than 24 hours.
5. Cervical cap

The cervical cap is placed in the vagina up to 6 hours before intercourse, and is 71–86% effective. These caps will only be available by prescription as the pharmacy needs to make sure the uterus is the right size for you. If you used the cap before getting pregnant, you will need to re-adjust the size of the hat. This is because your cervix changes after pregnancy and childbirth.
The cervical cap should be accompanied by a spermicide for maximum effectiveness. This means you can be 30% more likely to conceive if not taken with spermicide.
6. Diaphragm
This is a small pregnancy-prevention silicone pad that you use to insert into your vagina 2 hours before sex. It fits well into the cervix, helping you to prevent sperm from reaching the uterus. Your doctor will fit this silicone sheet and resize you after your baby is born, because by that time your cervix has changed and the diaphragm size is no longer suitable.
This method is only effective about 60% for women who have had children. For best results, always use the spermicide with the diaphragm!
7. Condom

Condoms work by keeping sperm from entering the vagina. They come in many types, including:
Male condom or female condom
Made of rubber or not rubber
No lubrication or lubrication
Kill sperm.
Condoms are also the only form of birth control that helps protect against sexually transmitted diseases.
When used correctly, condoms are up to 98% effective. Proper use means you should use a condom every time you have sex from start to finish. In other words, you are not allowed to have any sexual activity before wearing a condom. Correct use also includes condoms that do not tear or fall out during sex.
With normal use, that number drops to around 82% efficiency. This explains all accidents that happen during intercourse. For extra protection, use a condom with other birth control methods like spermicide or family planning.
8. Plan of IUD insertion (IUD)
IUD insertion is more than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy. Therefore, it can be said that this is the most effective birth control method on the market. The IUD is a form of permanent contraception and can be easily removed (LARC). The IUD is made up of two different types of hormone and non-hormone. You can only use it with your doctor's permission.
The hormonal contraceptive ring
In the composition of the hormonal IUD contains progestin. This is the synthetic form of the hormone progesterone. This hormone increases cervical mucus to help keep sperm from reaching the uterus. The following types of IUDs are available on the market:
Mirena : contraception up to 5 years
Skyla: contraception up to 3 years
Liletta: contraception up to 3 years
Kyleena: contraception up to 5 years.
Your doctor will help you insert a plastic T-shaped device into your uterus to prevent fertilization. However, when a foreign object is inserted into your body, your risk of becoming infected is greater. Therefore, the IUD is not a good choice for women with many sex partners.
The hormonal ring can also make your period lighter. Some women can stop their periods completely thanks to this method.
Non-hormonal IUD
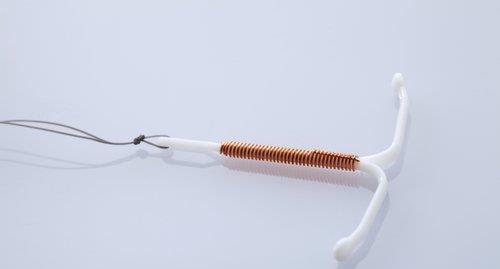
Paragard is the only non-hormonal IUD available today. Paragard uses a small amount of copper which makes it difficult for the sperm to move, which helps to prevent fertilization. Paragard has a contraceptive capacity of up to 10 years. However, IUD IUD may not suit you if you are often a lot of periods or had severe cramps. Many women who use copper-containing IUD report more prolonged and heavier periods.
You can put on the IUD right after birth, but ask your doctor if you really should. Many doctors recommend that you wait until your wound is completely healed and stop bleeding within 2-6 weeks after giving birth. This is because if you put it too early it can break and put you at risk of infection.
The IUD can cause side effects such as spasm after it is inserted, unusual or heavy bleeding, and bleeding between periods. These side effects are usually present within the first 6 months of insertion.
9. Contraceptive implants
Nexplanon implant contraceptive method is up to 99% effective. This small stick-shaped device is about the size of a matchstick. Your doctor will implant the contraceptive stick under the skin of your arm. Once in place, the implant can help prevent pregnancy for up to 4 years.
Contraceptive implants contain the hormone progestin, which works to help prevent ovulation. It also helps to thicken cervical mucus , preventing sperm from reaching the egg. You can insert the contraceptive implant right after giving birth and remove it if you want to get pregnant again.
Although complications with the Nexplanon contraceptive implant are rare, you should still let your doctor know if you feel:
Arm pain
Show signs of infection , such as fever or cold
Unusually heavy vaginal bleeding.
Hope this article has provided you with useful information about contraceptive methods while breastfeeding safely.
















