The umbilical cord connects the mother to the fetal body, containing 10 times more stem cells than bone marrow in an adult. In fact, when well nourished and protected, the role of the umbilical cord can help ward off many life-threatening conditions such as leukemia (leukemia), lymphoma, and bone marrow disorders.
From the first moment when the embryo attaches to the uterine wall until the baby is born, the umbilical cord plays a very important role for the fetus. This is a part about 50cm long, has the ability to heal and regenerate very well. To understand more about the role of umbilical cord, please refer to the following article of aFamilyToday Health .
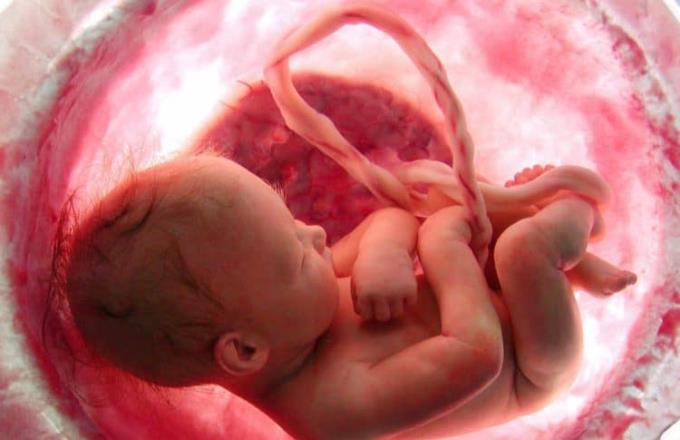
Formation and role of the umbilical cord
When a fertilized egg becomes a zygote, the zygote divides into two parts. Part of it will develop into a fetus in the womb. One part will become each other. As the fetus gradually matures, the umbilical cord is the bonding of these two parts together.
When you are 5 weeks pregnant, the umbilical cord is slowly forming. One end of the umbilical cord connects to the fetal abdomen, the other end will attach to the placenta.
In fact, the umbilical cord also helps form the placenta and binds to the uterine wall. It allows nutrients and oxygen to be transported from the mother to the fetus, and discharges excess substances and hypoxic blood from the fetus to the mother.
The umbilical cord also ensures that the blood does not mix, helps the fetus survive and grows, and produces the hormone hCG that helps maintain a healthy pregnancy. When your baby is born, the umbilical cord will be removed by the doctor, the rest will dry and fall off after a few days.
The structure of the umbilical cord
Normally, the umbilical cord can be up to 50 to 60 cm long consisting of two layers of muscle tissue, with a smooth outer layer and an inner layer containing a mucus layer called Wharton's jelly containing umbilical cord stem cells. There are 3 main blood vessels located in the umbilical cord: 2 arteries and 1 vein. Veins carry oxygen-rich blood to the fetus and arteries carry oxygen-poor blood out of the fetus.
The umbilical cord connects to the fetus's abdomen, the blood vessels divide into two branches. One branch flows into the hepatic vein and the other to the aorta in the fetal heart. Both will form a cycle between the fetus and the placenta in the mother.
In rare cases, the umbilical cord may not develop properly, for example the umbilical cord is wrapped around the baby's neck, arms and legs during pregnancy or in labor. With twins, in particular, this can be even more dangerous because the two babies are in the same amniotic sac.
Umbilical cord abnormalities can be detected by ultrasound. Therefore, the doctor can check the function of the umbilical cord and intervene promptly.
Umbilical cord abnormalities may occur
In addition to limiting fetal growth, there are 5 problems with umbilical cord that can be detected by ultrasound as follows:
1. There is only 1 artery in the umbilical cord
Although this is rare, sometimes the umbilical cord will lack an artery. This condition can cause blood deprived of oxygen and nutrients along with excess product are not properly removed from the fetus. While many experts have not paid much attention to this condition, there still exist a number of effects on the health of the fetus including fetal defects, heart disease and chromosomal disorders, affecting the nervous system. and urinary tract. However, do not worry too much because ultrasound can detect this condition early and take appropriate intervention.
2. Cut the umbilical cord
During labor, as the fetus moves through the epithelium, sometimes the umbilical cord may come back and be compressed when the baby is born.
This can be dangerous because the blood supply is reduced or completely blocked, threatening the fetus if the baby is not born quickly.
3. Cystic umbilical cord
In rare cases, cysts may form in the umbilical cord and are detected only by ultrasound. This can cause chromosomal, kidney, and abdominal abnormalities in the fetus.
4. The umbilical cord is knotted
This is one of the most common abnormalities during pregnancy and labor. The umbilical cord is wrapped around the baby's neck, arm or leg. However, all doctors can remove the umbilical cord from the outside or remove it after the baby is born. In rare cases, the umbilical cord is tightly knotted, threatening the fetus's life because the supply of blood, oxygen and nutrients is stopped.
5. Striker blood vessels
The blood vessels in the umbilical cord are misplaced. These blood vessels may not be protected by the umbilical cord and slide down the fetus. This causes blood vessels to tear and lead to bleeding.
If a woman has vaginal bleeding in the second or third trimester, it could be due to the blood vessels of the striker. At this point, you should go to the hospital immediately for prompt intervention.
The role of umbilical cord blood
Umbilical cord blood is the blood transferred from a mother to the fetus, which is rich in stem cells that can later differentiate into many specialized cells, tissues and organs in the body. These cells can save a baby as well as other family members from deadly diseases.
Umbilical cord blood is extracted, tested and stored as soon as the baby is born. The procedure is quite simple, like when you have a blood drawn. The only difference is that blood is drawn from the umbilical cord shortly after birth and stored in the cord blood bank for use for future blood and immune abnormalities.
The role of umbilical cord blood storage
Umbilical cord blood is used to regenerate stem cells. This blood is also important for marrow or umbilical cord blood transplant to form hematopoietic stem cells.
This will help in cases of blood cancer or other hematological disorders where hematopoietic stem cell transplant or marrow transplant can help heal. The likelihood of a sibling being suitable is only about 25%, while your stem cells will be perfectly suited and become your own savior.
However, the storage of stem cells is quite expensive, more than 1,500 - 1,900 USD (about 34,000,000 - 43,000,000 VND). If someone in the family has a history of blood problems, or wants to make sure your baby is safe, you can store this cord blood when your baby is born.
How to take care of the umbilical cord

Let the cord to dry naturally
In the past, many people were advised to use alcohol to disinfect the baby's umbilical cord to help prevent bacteria from entering and keep the umbilical cord clean. However, a study by the US National Center for Biotechnology Information noted that using antiseptics to wash and clean a baby's umbilical cord after birth prolongs the dry and healing process. cord.
You should not cover the umbilical cord and let it air dry. This helps to promote natural healing of the umbilical cord. To help the cord to fall off quickly, simply let it dry naturally. When dressing your baby, wrap the diaper under the navel to avoid touching and irritating the wound.
Dry bath (sponge bath)
Dry baths are a better option for babies. This way, you won't get your umbilical cord wet and help it heal faster. Here's how to dry your baby. You should prepare baby shower gel, 1-2 towels, diapers, clothes and follow these steps:
Fill the bath tub with warm water
Place your baby on a flat surface, put a towel under his back, undress and gently wrap him with a towel.
Wet a towel, squeeze out water, gently wipe the baby's face, around the eyes and nose, no need to use shower gel.
Wipe your baby's hands, arms, feet and feet.
When wiping to the abdomen, you use a cotton swab, soaked in some saline, and wipe around the navel.
Turn the baby on his stomach, wipe his back and butt.
Open the diaper, wipe the genitals clean, apply diaper rash cream if needed.
Wear a new diaper for your baby.
If you want to wash your baby's hair, hold him in his arms, bring him close to the water bath, use a cup to wet his head. Rub shampoo, wash shampoo, dry head for baby. Get dressed for your baby.
You may need to dry bathe your baby until the umbilical cord falls out in weeks 2 - 3. After that, you can put your baby in a tub of water to bathe. To see how to practice dry bath, you can go here .
Let the belly button fall naturally
Until completely dry, the umbilical cord remains part of the baby's body. Therefore, be gentle and careful when cleaning the area around the baby's umbilical cord and let that part fall out naturally.
Also, if you notice that your belly button turns pink or red and swollen, you should see your baby's doctor right away. This could be a sign of an umbilical cord infection. Get checked if the cord has not fallen out after 4 weeks.













