Are you pregnant and does your ultrasound show the front placenta? You don't know what effect this has. Find out through the article aFamilyToday Health.
The placenta (also known as the placenta) is the organ that connects the fetus to the mother's uterine wall through the umbilical cord. The main job of the placenta is to transport nutrients, supply oxygen to the fetus and help eliminate fetal waste. In addition, the placenta plays an important role in protecting the baby from the risk of infection and secreting large amounts of female hormones to prevent uterine contractions that take place before the due date. Usually, the placenta attaches to the front or back of the uterus. However, there are many cases where the placenta is in an abnormal position.
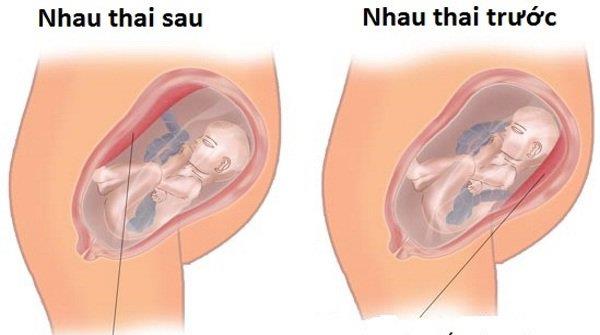
Placenta clinging to the front
Placenta placenta means that the placenta is located "just in front" of the baby's head. Normally, the placenta will form in the upper part of the uterus as soon as the egg is fertilized. However, sometimes the placenta develops and latches on to the lower part of the uterus, close to the abdomen. That means the placenta is in front and the fetus is right behind it.
Common sites of the placenta
An ultrasound in mid-pregnancy helps your doctor check the position of the placenta. Some common sites of the placenta:
Placenta front (in front of uterine wall)
Placenta placenta (behind the wall of the uterus)
The placenta sticks to the top of the uterine wall
The placenta attaches to the right or left side of the uterus.
These are the normal locations where the placenta usually develops.
Does the position of the placenta affect the baby?
This does not affect the baby at all. The position of the placenta no matter which side is located is not too different. However, if the placenta is attached to the front, there are a few problems with the placenta:
1. Difficulty in feeling your baby's movements
The anterior placenta will create the separation between the baby and the uterus. Therefore, you will not feel any movement in your baby. Even when entering the middle stage of pregnancy, you will not feel your baby's kicks.
2. Vegetables on the front side will be difficult to hear the baby's heartbeat

The unfavorable position of the placenta will make it difficult for the doctor to hear the baby's heart congestion. However, there is no problem with an ultrasound to determine the sex of the fetus .
3. Interfering with medical procedures
Placenta placenta will interfere with medical procedures. If the baby is inverted (buttocks front), the placenta sticking to the front will prevent the baby from being carried out.
All of these situations are resolved if the placenta returns to its posterior position at the end of pregnancy. Despite the aforementioned difficulties, the placenta sticking forward does not harm the health of mother and baby.
When do you feel your baby's movements?
If the placenta sticks to the front, the time you can feel your baby's movements will be slower than with normal pregnancies. Normally, pregnant women will feel the baby's movements clearly at 22 weeks. But if the placenta sticks to the front, you will feel the baby's movements around 24 weeks.
If after 24 weeks you still can't feel your baby's movements, see your doctor to ask about your situation. Your baby will continue to grow over the next few weeks so you will often feel your baby's kicks.
Placenta placenta has limitations?
Your doctor will monitor the uterus with an ultrasound between weeks 32 and 36 to check the placenta position. It is possible to have a normal birth if by the end of the pregnancy the baby moves to the right position. However, there are a few issues to keep in mind:
1. Each other striker
If during weeks 33 and 34, the placenta does not move upward and remains relatively low in the uterus, it will lead to the placenta . Your doctor will conduct an ultrasound to determine the best position of the fetus, placenta and appoint you to have a cesarean section. Therefore, you must have regular prenatal visits to reduce your risk of preterm birth and pregnancy complications.
2. Labor pain and other complications
Some women experience lumbar pain and discomfort at birth. This symptom depends on the baby's location and your health. You will experience these pains if the baby is on the mother's abdomen or spine.
If you have had a cesarean section during your previous pregnancy, the next pregnancy may develop in the scar area and the uterine wall. This is a fairly rare condition, but with an ultrasound and an MRI it's completely diagnostic.
Placenta sticking in the front will cause a number of health complications such as diabetes, fetal growth retardation and increased blood pressure.
Is a caesarean section the only option if the placenta is placenta?
Caesarean section is not the only option when the placenta is attached to the front. However, if the placenta immediately blocks the mother's cervix, blocking the baby's way out, birth is often completely impossible.
Some conclusions about the case of the placenta clinging to the front
The cases of the placenta clinging to the front, the fetus is often heavier than normal. In addition, when the placenta is attached to the front, the mother usually gives birth to a girl.
Placenta placenta is not harmful to the baby during pregnancy but can increase the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, slow growth and stillbirth.
Women with type O blood are more likely to have a placenta attached to the front.
Sleeping position during conception also affects the position of the placenta.
Placenta placenta usually increases labor pain and increases the risk of a cesarean section. In addition, it is also the cause of delayed labor and postpartum complications such as postpartum haemorrhage .
What is the maturity of the placenta?
The maturity of the placenta is assessed on the development of the placenta by ultrasound. This reflects the growth of each other during pregnancy.
The placenta usually starts at zero in early pregnancy and will develop gradually.
Degree 0
Pregnancy is usually in the early stages of pregnancy, less than 18 weeks.
The amniotic fluid is straight, smooth, and doesn't crack.
The placenta is concentrated in one area
Grade 1
Pregnancy in the middle stage of pregnancy, from weeks 18 to 29 weeks.
The pre-mature stage of the placenta.
The amniotic membrane does not fracture, is well defined, has vibrations.
The placenta is randomly dispersed.
Grade 2
Pregnancy in the late stages of pregnancy, about after 30 weeks.
The amniotic fluid cracks more and becomes complete.
Grade 3
Pregnancy exceeds 39 weeks, the last stage in the development of the placenta.
Complete amniotic fluid.
The placenta is divided into cavities.
Factors influencing the health of the placenta

The placenta plays an important role in your baby's development. Complications of placental attachment position can lead to delayed fetal growth or stillbirth. Several factors affect the health of the placenta:
High Blood Pressure
Pregnant at the age of 40 and older
Pregnant many times
Surgery of the uterus before pregnancy
Pre-natal disorders
Problems with blood clotting
Drug use or other substance abuse during pregnancy
Injury to the abdomen.
Take care of the placenta
There are a few ways to take care of the placenta:
Avoid sudden strong jets. Wear seat belts when sitting in cars and planes. Avoid smoking as tobacco will harm the placenta and the fetus.
Eat plenty of green vegetables, whole grains , nuts like almonds, and foods with good fats like avocados. In addition, you should limit salt intake to processed foods instead of eating foods that are easy to digest.
Exercise only when your doctor says it is. Consult your doctor before doing prenatal Kegel, walking and yoga exercises.
Reduce sudden movements during pregnancy.
Periodic pregnancy check-up. Regular checkups will help doctors detect placenta early and take preventive measures.
If you experience abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding during pregnancy, get medical attention immediately. Abdominal pain is a common problem, but you should examine carefully to determine the cause of these attacks. If you experience pain due to the sloughing of the placenta and not be treated in time, it will cause death. Also, tell your doctor if you experience back pain, early uterine cramping or other pain in the abdomen.
Complications of the anterior placenta can be completely controlled if detected early. Do not worry too much if you fall into a placenta. All you need to do is follow your doctor's instructions, eat healthy, get plenty of rest and enjoy a great pregnancy.














